When purchasing galvanized steel coils, several key factors must be understood to ensure the right choice for your specific needs. Here are the primary considerations:
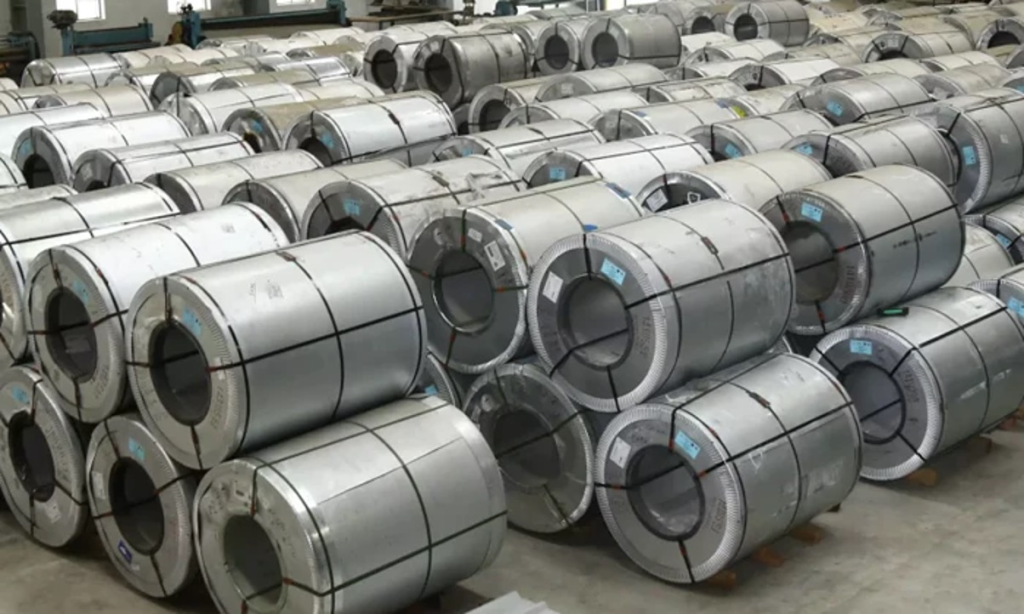

- Type of Galvanization:
- Hot-Dip Galvanized (HDG): This involves dipping the steel into a bath of molten zinc, resulting in a robust, thick coating. It is widely used for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. Ideal for outdoor and industrial applications.
- Electro-Galvanized: This uses electroplating to apply zinc, resulting in a thinner and more uniform coating compared to HDG. It offers a smoother surface finish, making it suitable for applications requiring precision and aesthetic appeal, like automotive parts and appliances.
- Coating Thickness (Zinc Coating Weight):
- Measured as g/m² or oz/ft². Common standards include G30, G60, G90, etc., where the number indicates the total weight of zinc on both sides of the steel sheet.
- Heavier Coatings: Provide better corrosion protection and are suitable for harsh environments. For example, G90 (275 g/m²) is commonly used for external applications.
- Lighter Coatings: Suitable for indoor use or environments with less exposure to corrosive elements.
- Steel Grade:
- Different grades provide varying mechanical properties.
- Commercial Quality (CQ): Suitable for general applications with no specific strength requirements.
- Drawing Quality (DQ): Offers better ductility and formability for parts requiring significant deformation.
- Structural Quality (SQ): Provides higher strength for load-bearing applications.
- High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA): Combines strength with formability and is often used in automotive and construction sectors.
- Surface Finish:
- Regular Spangle: Visible crystalline pattern that forms as the zinc cools. Acceptable for many applications but may not be suitable for painting.
- Minimized or Zero Spangle: Provides a smoother surface, often achieved by controlling the cooling process or using specific alloys. Better suited for painting and aesthetic applications.
- Surface Treatments: Passivation or chromating can be applied to improve corrosion resistance and paint adhesion.
- Dimensions and Tolerances:
- Precise specifications for width, thickness, and length are crucial.
- Common tolerances are specified by standards (e.g., ASTM A653 for galvanized sheets).
- Ensure the dimensions match the requirements of your processing equipment and final application.
- Coil Weight and Size:
- Standard coil weights can range from a few hundred kilograms to several tons.
- Inner Diameter: Typically around 508 mm (20 inches) or 610 mm (24 inches).
- Outer Diameter: Varies but must be compatible with your handling equipment.
- Formability and Weldability:
- Formability: Important for applications involving bending or shaping. The coating should adhere well to the steel during these processes without flaking.
- Weldability: Zinc can affect welding processes. Galvanized steel typically requires special procedures or filler materials to ensure strong welds and avoid defects.
- Corrosion Resistance:
- The environment plays a crucial role in determining the necessary coating weight.
- For coastal areas, higher coating weights are recommended due to the aggressive nature of salty air.
- Industrial environments may require coatings resistant to chemicals or pollutants.
- Supplier Reputation and Certification:
- Choose suppliers with certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management.
- Request mill test reports (MTRs) or certificates of compliance to verify material properties and standards adherence.
- Cost:
- Analyze the cost against the performance requirements. While thicker coatings and higher grades increase costs, they also provide longer life and better performance in demanding environments.
- Logistics and Availability:
- Factor in lead times, especially for large orders or custom specifications.
- Consider the supplier’s location relative to your operations to minimize shipping costs and delivery times.
- Environmental and Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensure the material meets environmental regulations, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) if applicable.
- For specific industries like automotive or construction, compliance with additional standards (e.g., REACH, LEED) might be required.
Understanding these detailed aspects will enable you to make well-informed decisions when purchasing galvanized steel coils, ensuring that the material you select meets your performance, quality, and budgetary requirements.


